name: title layout: true class: center, middle, style1 --- <h1 style="font-weight: 600"> TOWARDS AN ENERGETIC THEORY OF ISLAND BIOGEOGRAPHY </h1> <br/><br/> ### ESA annual meeting - August 9<sup>th</sup>, 2018 <br> ### .left[ [KCazelles](http://kevincazelles.fr)] ### .left[ .small[[KevCaz/talkETIB](https://github.com/KevCaz/talkBES2017)]] .right[[inSileco](https://inSileco.github.io/)] <img src="img/inSilecoLogo.png" height="120" align="right" style="padding:8px"/> <img src="img/logoUniv.png" height="120" align="right" style="padding:12px"/> ### .left[Kevin S. McCann] ### .left[Domique Gravel] --- name: style2 layout: true class: center middle, style2 --- # CONTEXT <hr/> ### Biogeography: processes and distributions --- name: style1 layout: true class: style1 --- # Biogeography: processes <hr/> .center[] --- # Biogeography: processes <hr/> .center[] --- # Biogeography: processes <hr/> .center[] --- # Biogeography: processes <hr/> .center[] --- # Biogeography: distributions <hr/> .center[] --- # Biogeography: distributions <hr/> .center[] --- # Biogeography: questions <hr/><br/> ### How processes generate distributions? ### How to infer processes from distributions? <br> --- # Biogeography: theories <hr/><br/> ### 1. Theory of Island Biogeography (TIB) ### 2. Neutral Theory of Biogeography (NTB) -- ###  Within 1 trophic level -- <br> ###  More than 1 trophic level? ####  [Holt, *Toward a Trophic Island Biogeography* (book chapter), 2009.](https://press.princeton.edu/titles/9096.html) ####  [Gravel *et al.*, *Ecology Letters*, 2011.](http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01667.x/abstract) ####  [Cazelles *et al.*, *Ecography*, 2016.](http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ecog.01714/abstract) #### [Massol *et al.*, *Advances in Ecological Research*, 2017.](https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aecr.2016.10.004) --- # Biogeography: initial questions <hr/><br/> ###  How to include more trophic levels? ###  How to include ecological interactions? --- name: style2 layout: true class: center, middle, style2 --- # Biogeography & biotic interactions <hr /> ### Integrating ecological network --- name: style1 layout: true class: style1 --- # Theory of Island Biogeography (TIB) <hr/><br/> .center[] --- # Theory of Island Biogeography (TIB) <hr/><br/> .center[] ??? Powerful vision but strong assumption ??? première étape pour lever l'hypothèse. --- # Networks and TIB <hr/><br/> .center[] .small[ [Cazelles *et al.*, *Ecography*, 2016.](http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ecog.01714/abstract)] --- # Networks and TIB <hr/><br/> .center[] .small[ [Cazelles *et al.*, *Ecography*, 2016.](http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ecog.01714/abstract)] --- # Networks and TIB <hr/><br/> .center[] .small[ [Cazelles *et al.*, *Ecography*, 2016.](http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ecog.01714/abstract)] --- # What did we learn? <hr/> -- ## Theoretical models with >1 trophic levels raise tons of questions <br> -- ## What is predictable? <br> -- ## Where/What are the constraints? <br> -- ## Energy! input / flux / existing theories <!-- Stability / MVP and population cosumption --> <!-- May the probability of max trophic length is easier than exact composition --> <!-- Maybe a given composition of species --> --- name: style2 layout: true class: center, middle, style2 --- # Building an Energetic Theory of Island Biogeography <hr /> ### A key to integrate them all --- name: style1 layout: true class: style1 --- # A truism? <hr/> .center[] --- # A truism? <hr/><br> ## Sun  Autotrophs  Hetreotrophs <br> -- ## Water, carbon, nutrients availability <br> --  [Elton, *Journal of Experimental Biology*, 1924.](http://jeb.biologists.org/content/2/1/119) --- # Constraining the model <hr/><br> .center[] --- # Constraining the model <hr/><br> ## - 1 island = limited input of energy (J.s<sup>-1</sup>) <br> -- ## - a foodweb has an energy cost <br> -- ## - reaching the energy limit triggers an extinction --- # Energy cost of a network on an island <hr/><br> .column[ <br> - simulated food webs - body size constrains: - energy cost of a population (cM<sup>3/4</sup>) - topology of the food web ] .column[] --- # Energy cost of a network on an island <hr/><br> .column[ <br> - Explicit energy transfer Φ ] .column[] --- # Energy cost of a network on an island <hr/><br> .column[ <br> - Energy to sustain minimal viable populations (MVP) ] .column[] --- # Energy cost of a network on an island <hr/><br> .column[ <br> - Energy to sustain minimal viable populations (MVP) - Otherwise, extinctions! 1. random 2. the most costly species ] .column[] --- # Energy cost of a network on an island <hr/><br> .column[ <br> - most costly species? ] .column[] --- # Cost of a community on an island <hr/> .center[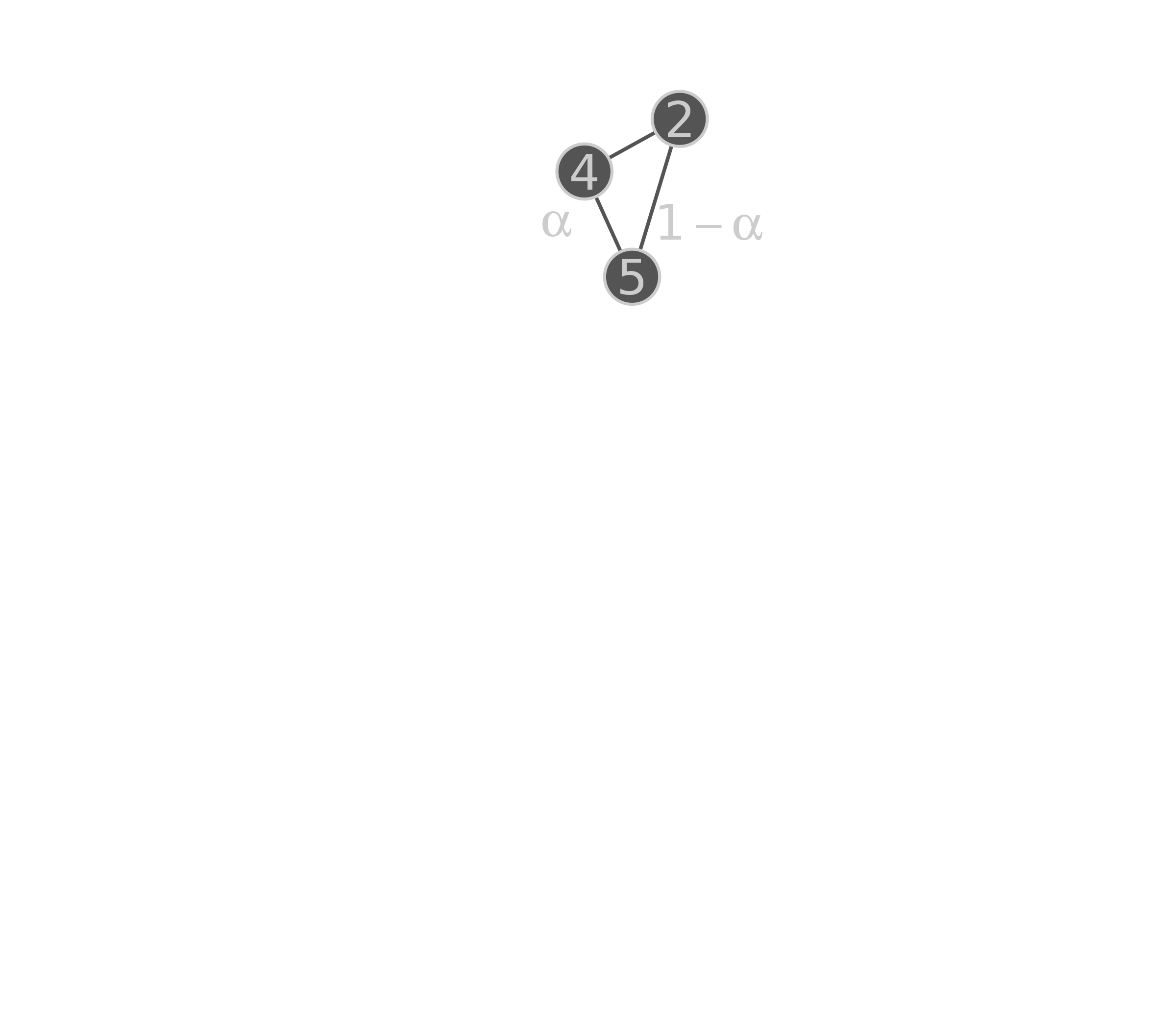] --- # Cost of a community on an island <hr/> .center[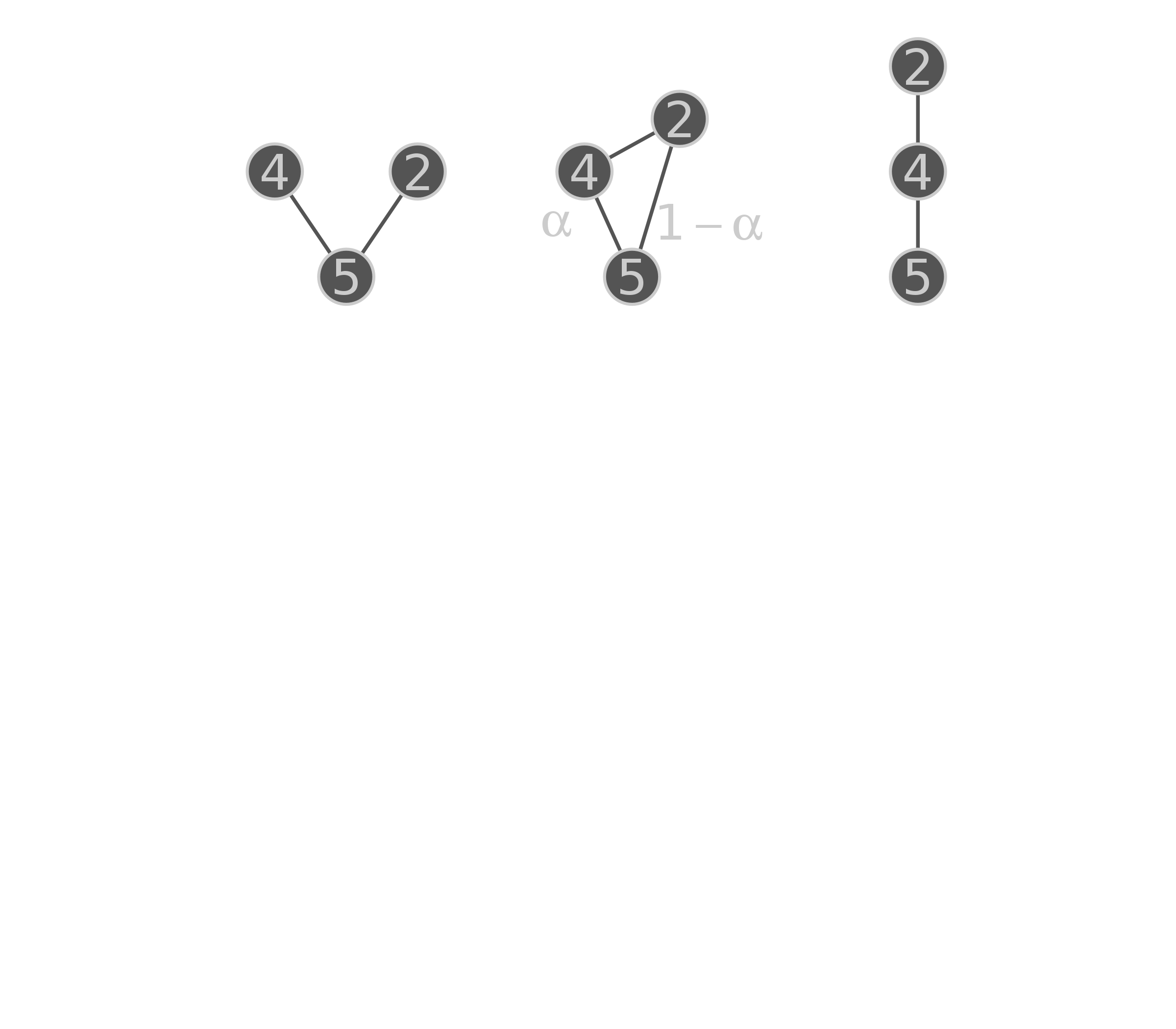] --- # Cost of a community on an island <hr/> .center[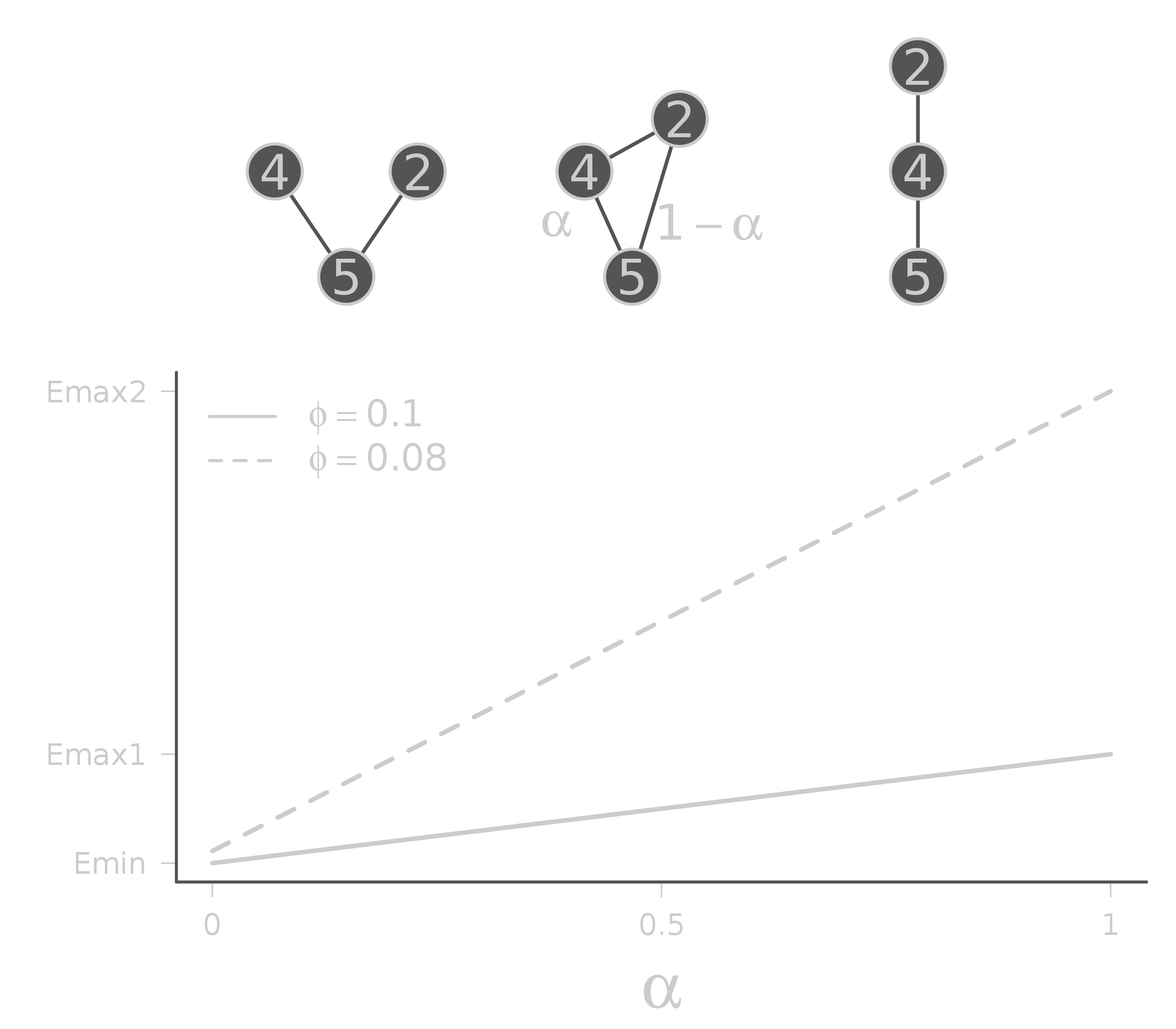] --- # SARs become SERs .small[ [Wright, *Oikos*, 1983.](https://www.jstor.org/stable/3544109)] <hr/> .center[] --- # SARs become SERs <hr/> .center[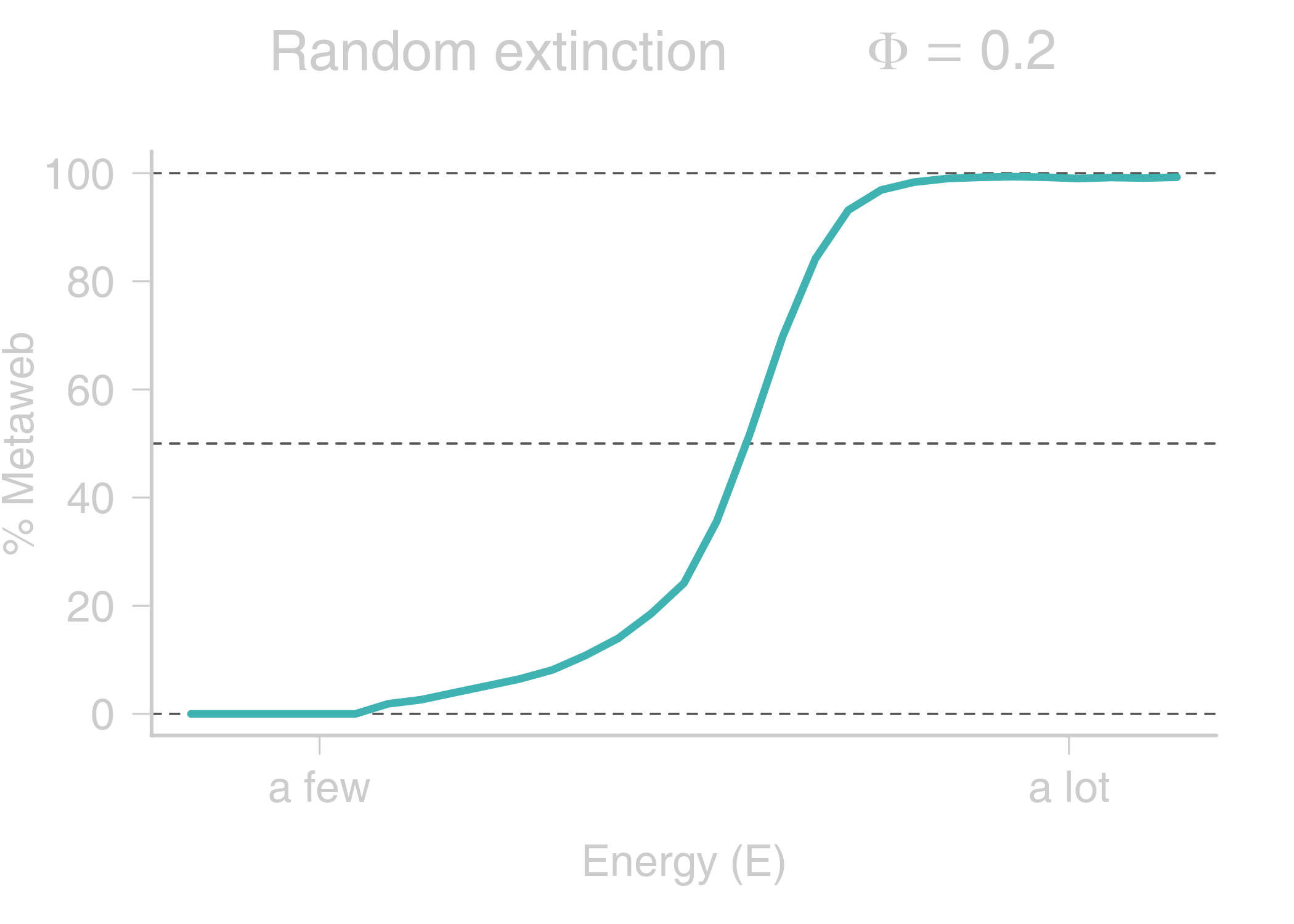] --- # SARs become SERs <hr/> .center[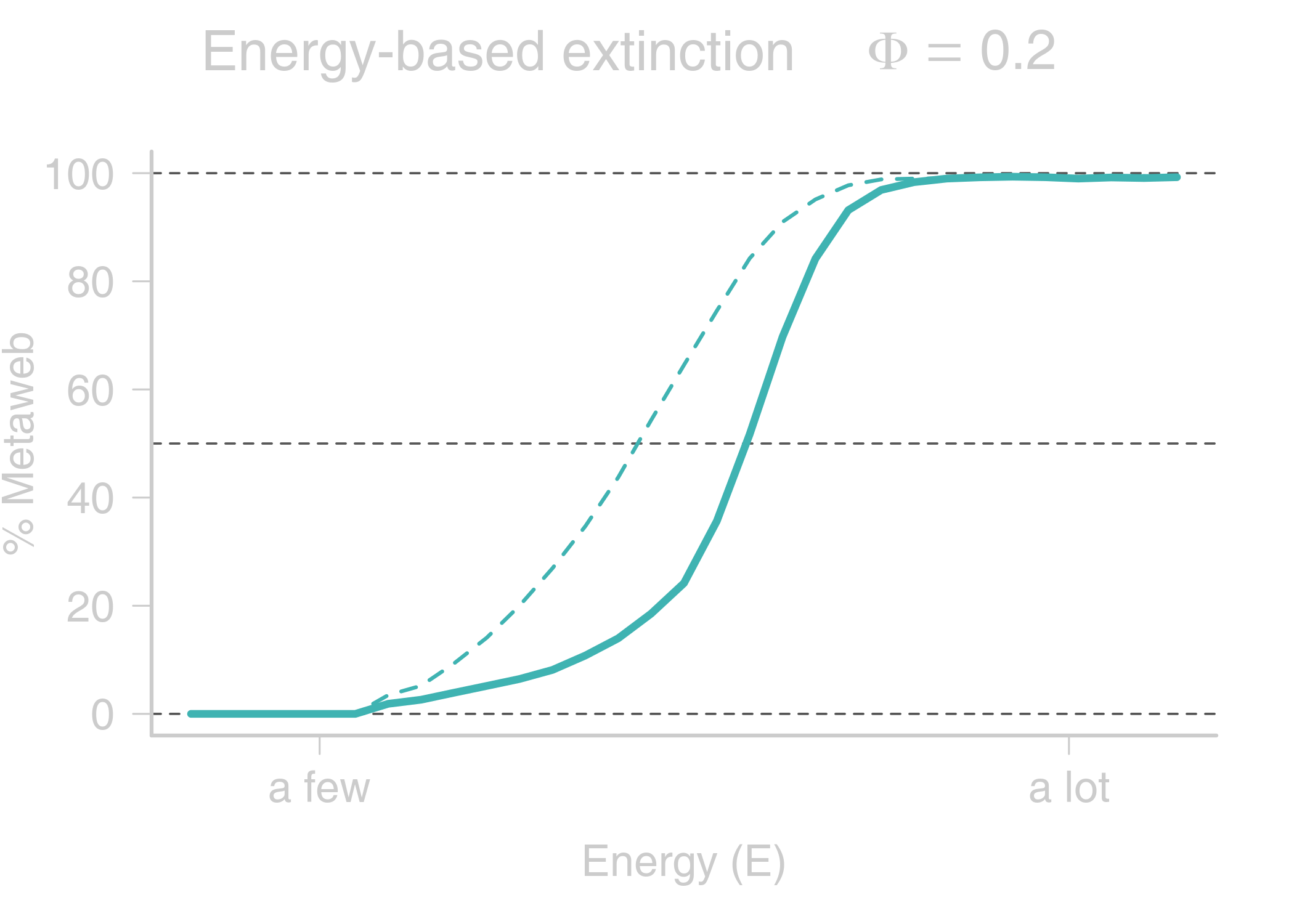] --- # SARs become SERs <hr/> .center[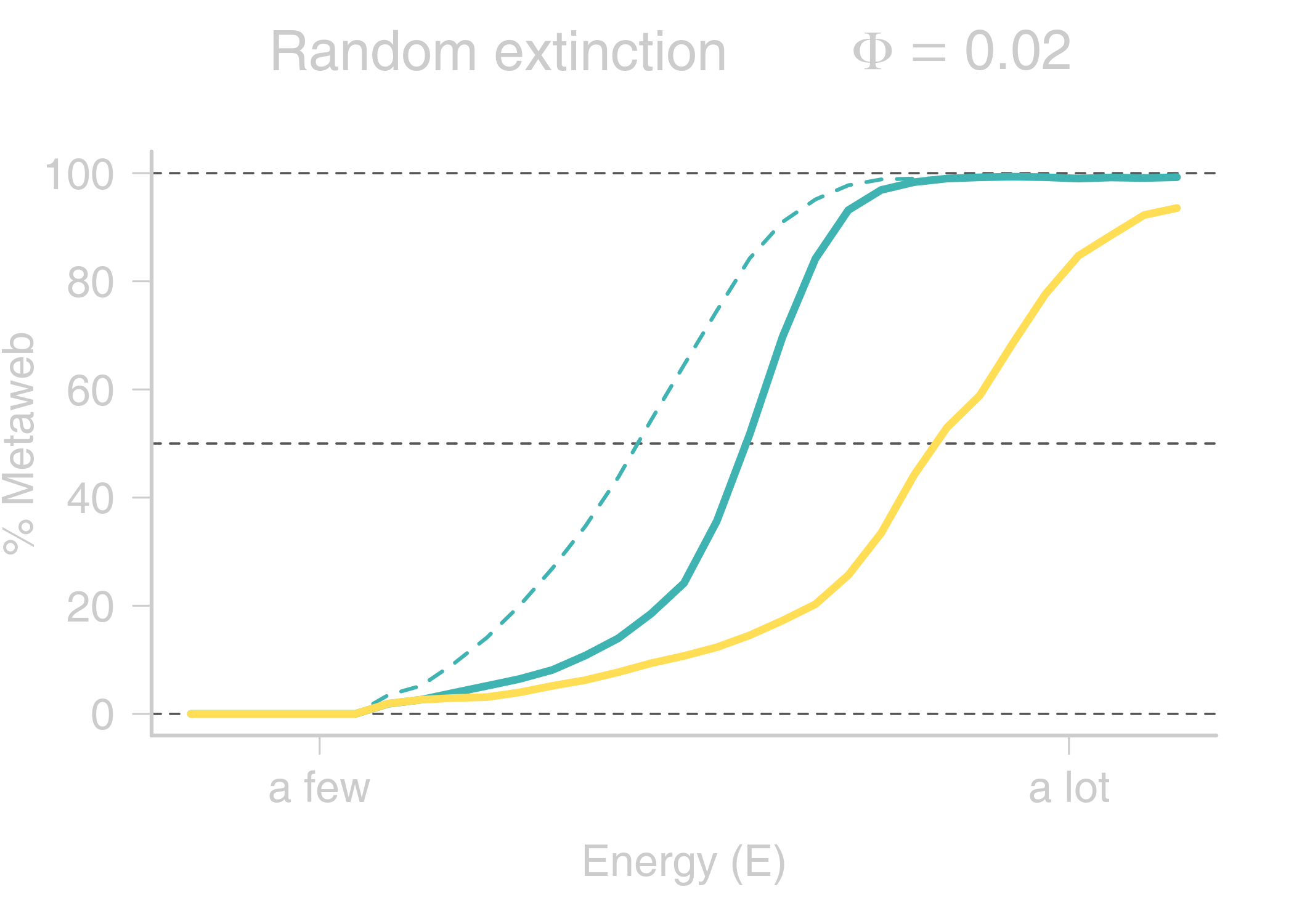] --- # SARs become SERs <hr/> .center[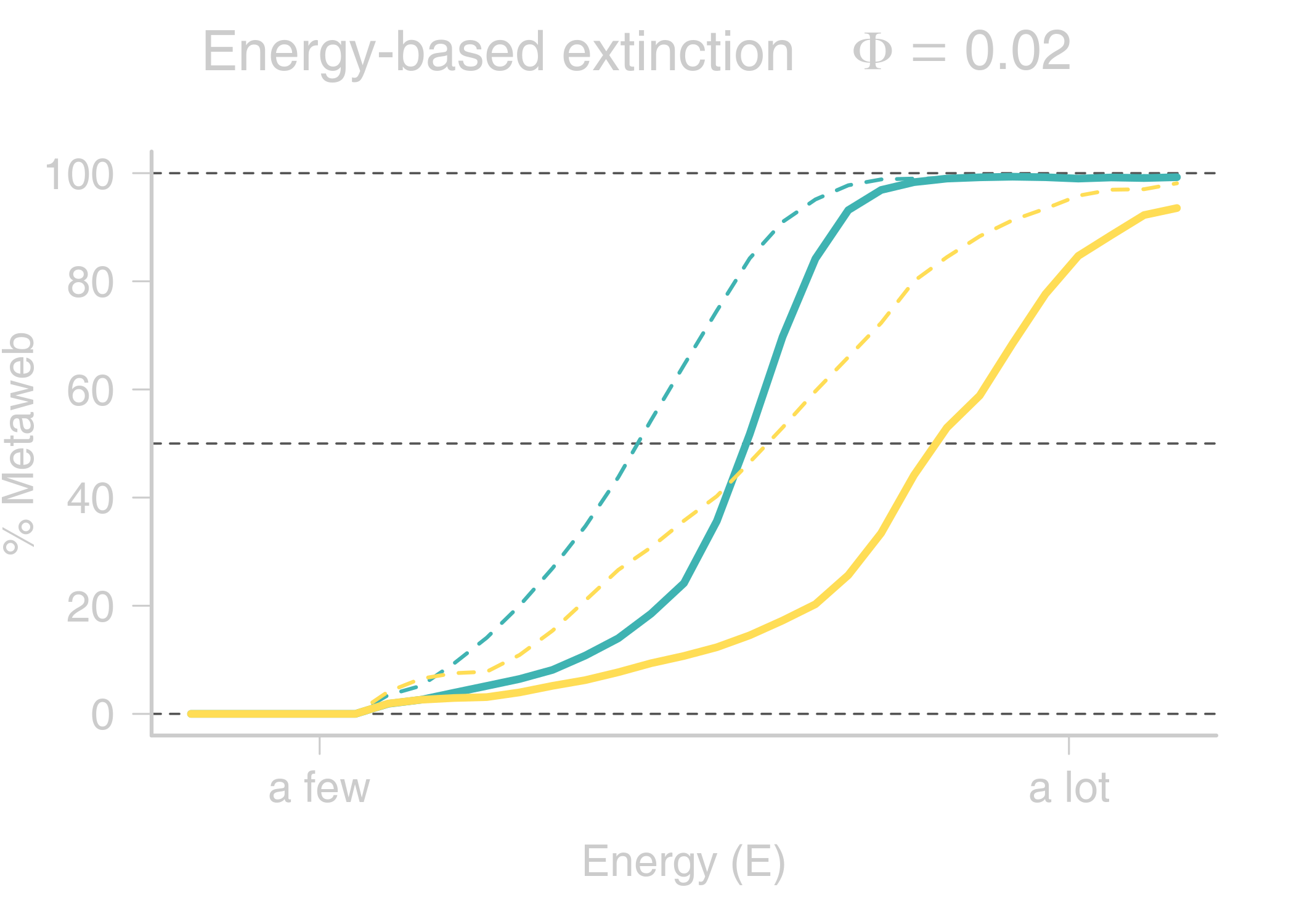] --- # Mean degree <hr/> .center[] --- # Mean degree <hr/> .center[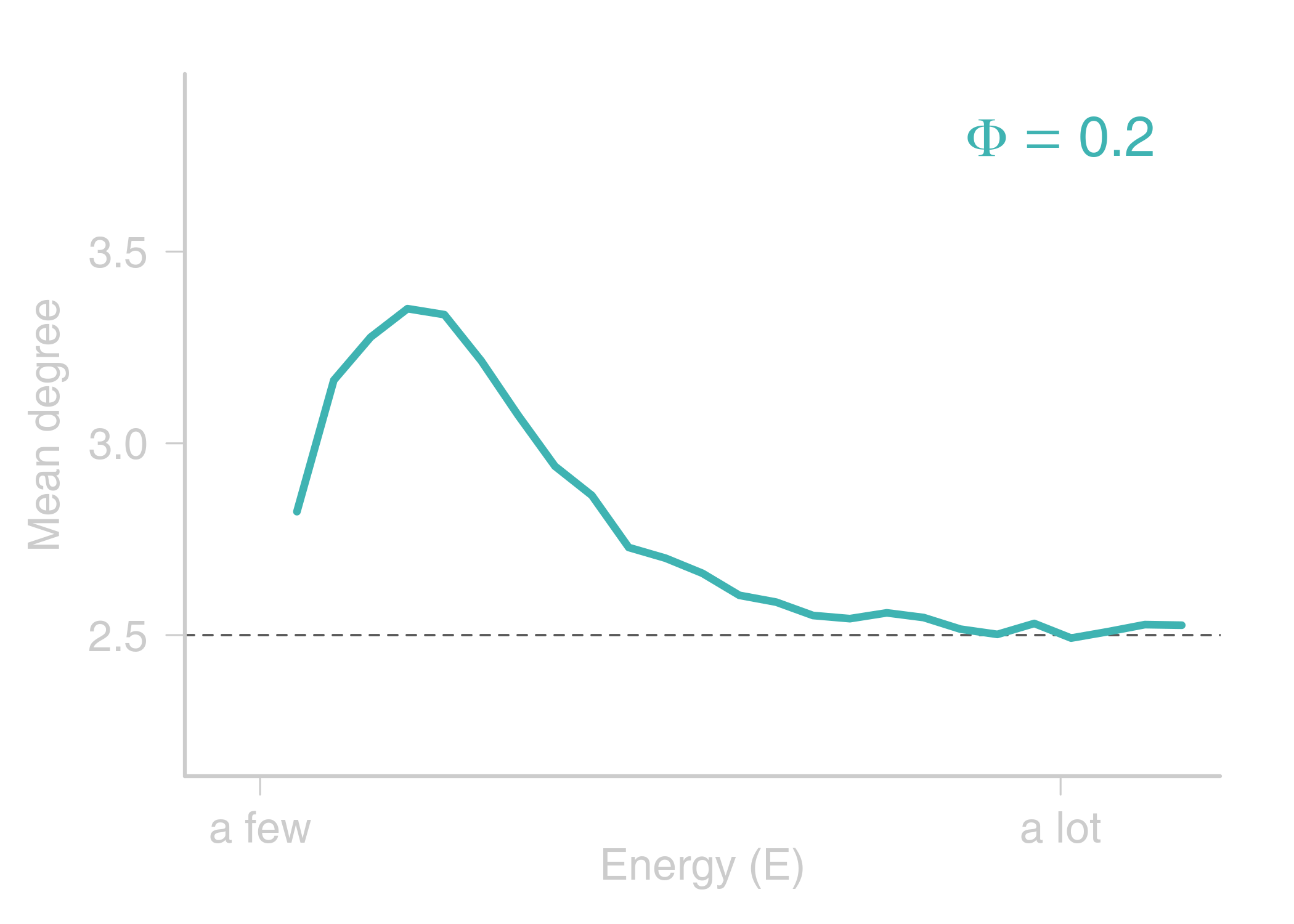] --- # Mean degree <hr/> .center[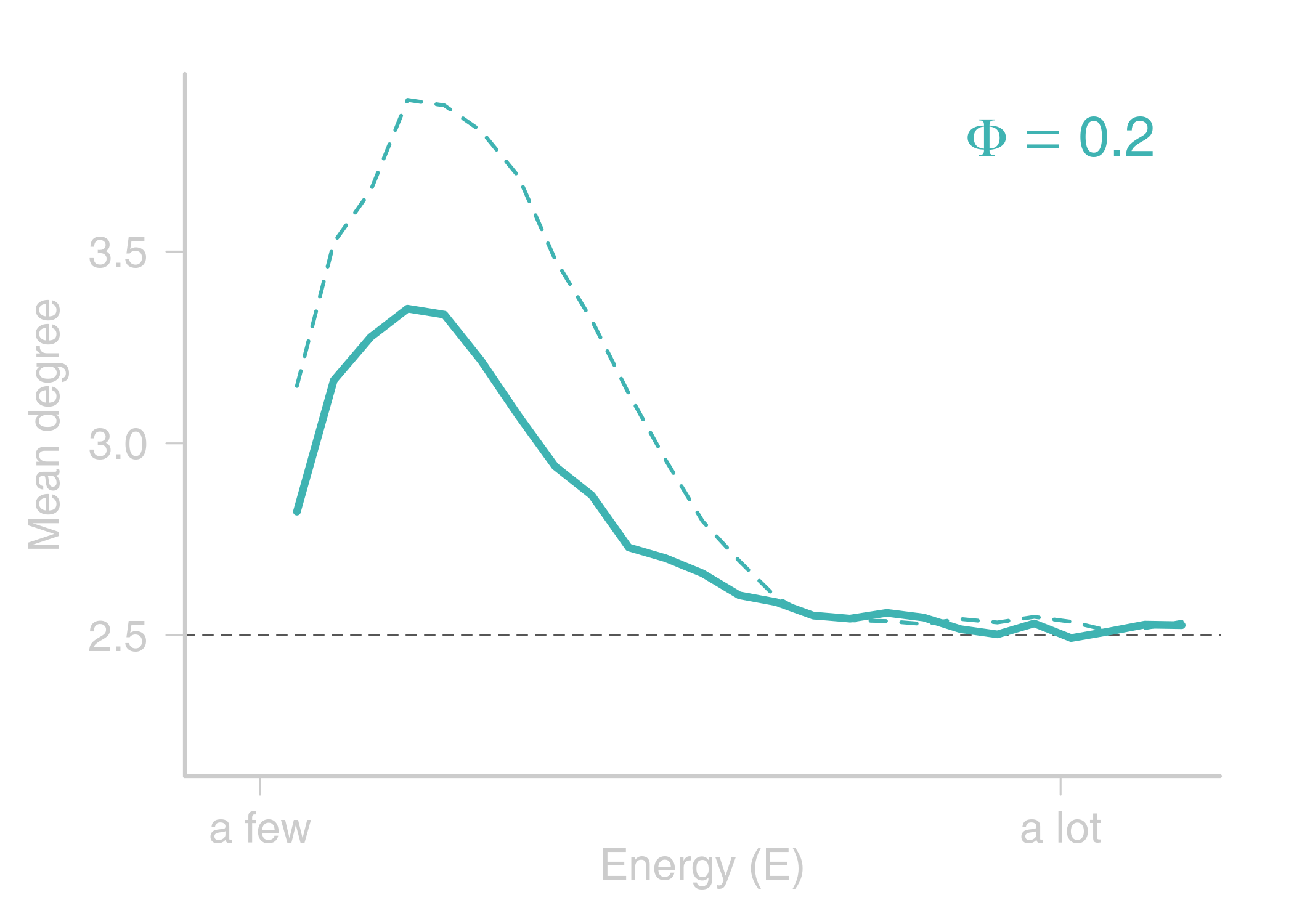] --- # Mean degree .small[[Piechnik *et al.*, *Oikos*, 2008.](https://www.jstor.org/stable/3544109)] <hr/> .center[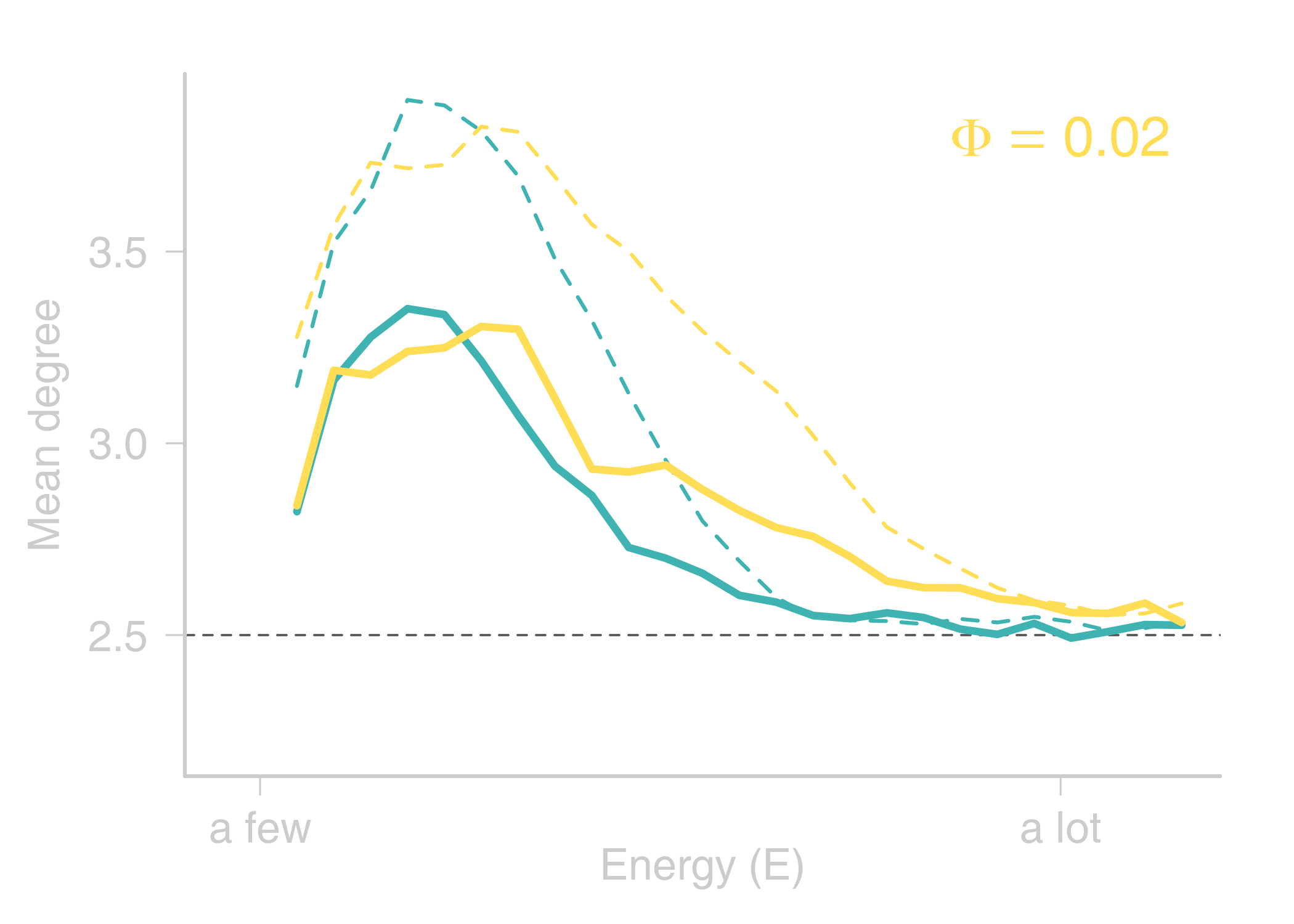] <!-- contrast random and non randon scenarios --> --- name: style2 layout: true class: center, middle, style2 --- # How ETIB could be useful? <hr /> ### Concluding remarks and perspectives --- name: style1 layout: true class: style1 --- # Quantification across trophic levels <hr/><br> ## To do so, ETIB should: -- ### 1. include a global energy constraint  zero-sum in NTB -- ### 2. describe the structure of energy flux  [Barnes, A. D. *et al.* (2018). Energy Flux: The Link between Multitrophic Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning. *Trends in Ecology & Evolution*.](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29325921) -- ### 3. support the development of the biogeography of food webs  [Galiana, N., *et al.* (2018). The spatial scaling of species interaction networks. *Nature Ecology & Evolution*.](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41559-018-0517-3) --- # Explain intriguing relationships <hr/><br> .center[] --- # Help forecasting biodiversity <hr/> .center[] --- name: style2 layout: true class: center, middle, style2 --- # THE END - THANKS! <hr> <br><br> 